TL;DR
Connected mobility links vehicles, infrastructure, and users through advanced communication for real-time data exchange, improving safety, efficiency, and user experience. It involves vehicle sensors, communication networks (cellular, V2X), infrastructure devices, cloud data platforms, and applications for drivers, fleet managers, and others. Key elements include IoT-enabled vehicles, telematics, V2X communication, edge analytics for low-latency processing, AI-driven insights, and strong cybersecurity. Zeliot’s Condense (cloud) and Condense Edge (edge computing) platforms support scalable, real-time data management and analytics, enabling quicker decision-making near the vehicle and reducing cloud dependence. Together, they address data privacy, infrastructure, and processing challenges, advancing connected mobility for safer and more efficient transportation.
Connected mobility represents a transformative shift in transportation, where vehicles, infrastructure, and users are seamlessly linked through advanced communication technologies. This interconnectivity facilitates the exchange of data, enabling real-time decision-making, and optimizing transportation systems for safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
Imagine a world where vehicles communicate seamlessly with each other, with infrastructure, and with external systems to provide a safer, more efficient, and enjoyable driving experience. This is the promise of automotive connected mobility. As vehicles evolve from standalone machines to interconnected nodes in a vast mobility network, the implications for safety, efficiency, and user experience are significant.
Architecture of Connected Mobility

A robust connected mobility system relies on a well-defined architecture comprising several interconnected layers:
Vehicle Layer: This layer encompasses the vehicle's onboard systems, including sensors, actuators, control units, and telematics devices. These components collect and process data related to vehicle performance, driver behaviour, and environmental conditions.
Communication Network Layer: Responsible for transmitting data between vehicles, infrastructure, and external systems. This layer utilizes various communication technologies such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, Dedicated Short-Range Communication (DSRC), and Vehicle-to-X (V2X) protocols.
Infrastructure Layer: Consists of roadside units, traffic management systems, IOT devices, Smart home devices and other infrastructure components that support connected mobility services. Infrastructure Layer creates a robust foundation for connected mobility services, enabling a wide range of applications and enhancing the overall transportation experience.
Cloud Platform Layer: Centralized platform for data storage, processing, and analysis. It enables advanced applications and services, such as predictive maintenance, traffic optimization, and autonomous driving.
Application Layer: Houses the various applications and services that leverage connected mobility data. These applications cater to different user segments, including drivers, passengers, fleet managers, Insurance companies and city planners.
Crucial Components of Connected Mobility
Internet of Things (IoT) in Vehicles
The foundation of connected mobility lies in the integration of IoT devices within vehicles. Sensors and smart devices collect and transmit data on various aspects such as vehicle performance, driver behavior, and environmental conditions. This data is crucial for enabling real-time decision-making and enhancing vehicle functionality.
Telematics and Connectivity Solutions
Telematics systems enable vehicles to communicate with external systems, providing features like remote diagnostics, navigation, and infotainment. These systems rely on cellular, satellite, and other communication technologies to ensure constant connectivity and data exchange, enhancing the overall driving experience.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication extends connectivity beyond the vehicle to encompass interaction with other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), pedestrians (V2P), and the network (V2N). This interconnectedness allows for the exchange of critical information, such as traffic conditions and hazard warnings, paving the way for safer and more efficient roadways.
Edge Analytics
Traditionally, data collected by telematics devices is sent to centralized cloud servers for processing. However, the inclusion of edge analytics in telematics devices allows for quicker analysis at the source. By processing data locally within the vehicle, edge analytics reduces latency and enables real-time decision-making. This approach is particularly beneficial for event flagging and applications requiring immediate responses, such as collision avoidance, Fuel theft / pilferage, and emergency braking systems.
Data Analytics and AI
The vast amounts of data generated by connected vehicles require robust analytics and AI algorithms to extract meaningful insights. Predictive maintenance, for example, leverages AI to forecast potential vehicle issues before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs. Similarly, data-driven insights contribute to enhancing safety measures and optimizing route planning.
Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Protecting vehicle data and ensuring the integrity of communication channels are paramount to prevent cyberattacks. Advanced encryption, secure communication protocols, and constant monitoring are essential to safeguarding connected mobility ecosystems.
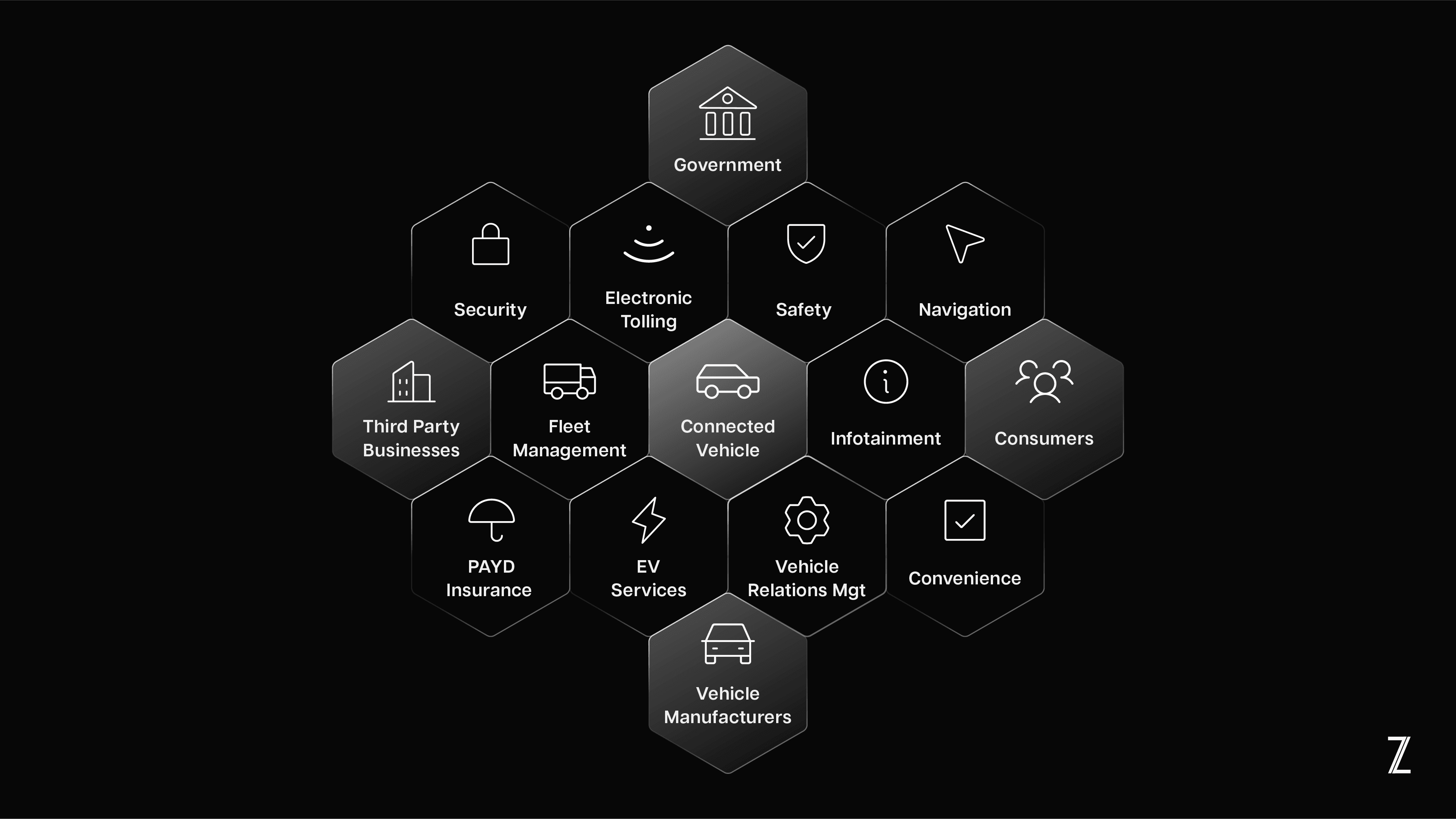
Ecosystem of Connected Mobility
The connected mobility ecosystem encompasses a wide range of stakeholders:
Vehicle Manufacturers: Develop connected vehicle technologies and platforms.
Telecommunication Providers: Offer connectivity solutions and network infrastructure.
Infrastructure Providers: Deploy and maintain roadside units and other infrastructure components.
Software and Service Providers: Develop applications and services for connected mobility.
Government Agencies: Regulate the industry, develop policies, and invest in infrastructure.
End Users: Benefit from connected mobility services, including drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
Condense and Condense Edge for Connected Mobility
Zeliot's Condense and Condense Edge are products designed to accelerate the development ecosystem and deployment of connected mobility solutions.

Condense is a cloud-based platform designed for efficient data management and analysis. It offers real-time analytics, a user-friendly interface, and robust scalability to handle the vast and rapidly growing datasets generated by connected vehicles. Condense simplifies building of data pipeline from data ingestion, processing, and till export, empowering users to extract valuable insights with ease.

Condense Edge is an edge computing solution that enables data processing closer to the vehicle, Condense Edge significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time decision-making for critical functions. Through advanced edge analytics and event flagging, it prioritizes data transmission, minimizing cloud reliance and improving operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Automotive connected mobility marks a revolutionary shift in how we perceive and interact with vehicles. By leveraging connectivity, data analytics, and AI, connected vehicles provide unparalleled safety, efficiency, and user experience benefits. The addition of edge analytics in telematics devices like Condense Edge further enhances these advantages by enabling real-time data processing at the source. While challenges such as data privacy and infrastructure development are addressed by robust platforms like Condense, the ecosystem continues to evolve, making connected mobility a fundamental part of our transportation landscape and transforming the way we move and live.
About Zeliot
Running ML models and AI algorithms on batch data is like watching a movie on a floppy disk. Zeliot is transforming this outdated approach with flagship products, Condense and Condense Edge. These platforms empower enterprises to manage business operations with real-time data, run algorithms on data received from sources at the highest frequency like never before, and provide 100% data control, with seamless data localization and ironclad privacy protection.





